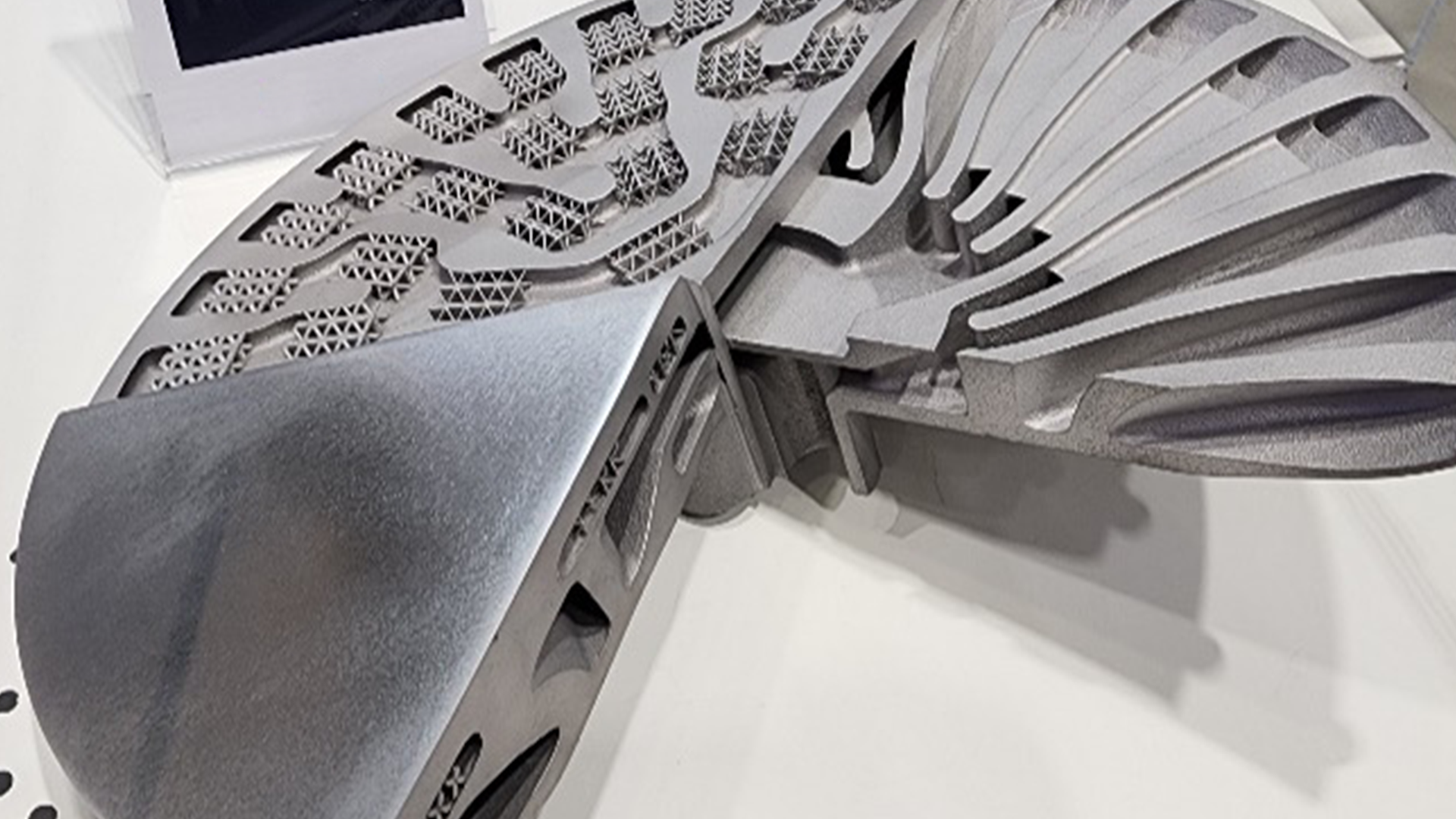
Additive manufacturing (metal 3D printing) technology has been in the spotlight as a next-generation technology while attracting attention to 3D printing technology using existing polymers. As the technology is actually used in the aviation field, the scope of application of additive manufacturing has also greatly expanded. However, metal 3D printing technology is still an advanced technology, and in Korea, the infrastructure, scope of application, and understanding of the technology lag behind other developed countries, and there is no actual related expertise. There is a lack of education and processes.
To compensate for this, Colibrium Additive (Formerly GE Additive), a leader in the metal 3D printing field, provides comprehensive one-stop services. To help with actual industrialization, we generously provide a variety of support, from consulting, including training, to material provision. In the case of consulting, information about the metal 3D printing industry and basics called 'Discovery Workshop' is shared with clients, followed by an in-depth course called 'Design Workshop', a course on various processes necessary for the actual industrialization stage. It even provides an ‘Industrialization Workshop’.
In addition, since we provide metal powder (material) from AP&C, which Colibrium Additive acquired, we can complete high-quality products. AP&C's powders are of excellent quality because they are made into spherical powders using a plasma method, unlike other powder manufacturers who make them using a gas method.
In fact, examples of industrialization using metal 3D printing are emerging by utilizing Colibrium Additive’s one-stop service. In the space field, which has recently been in the spotlight, domestic companies are achieving rapid growth through the application of metal 3D printing technology.
Staco, domestic metal 3D printing technology... Contributed to the success of Korea’s first private rocket launch.
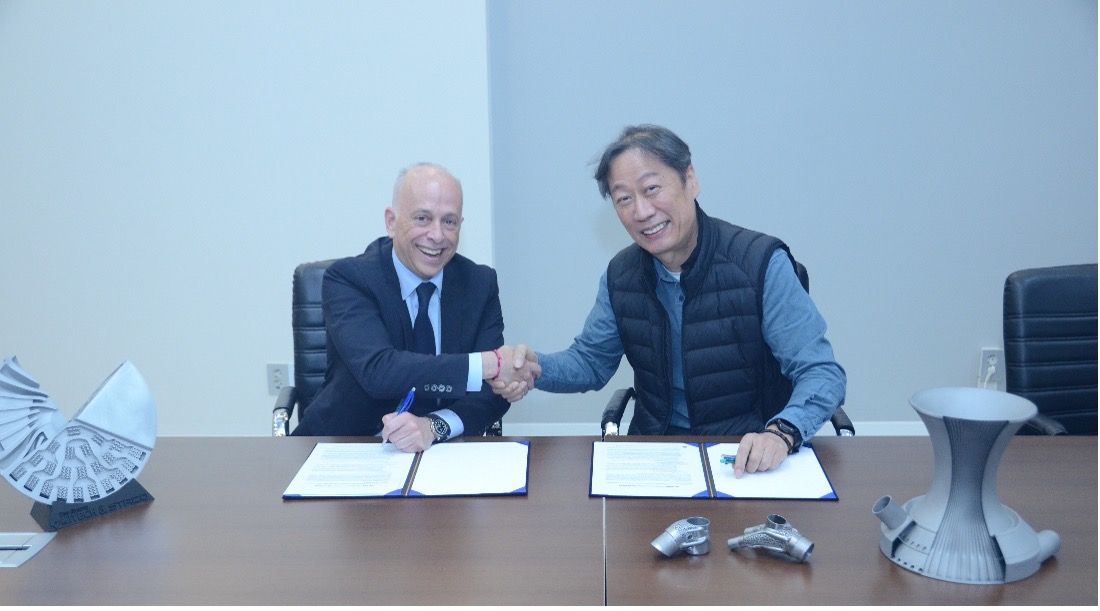

Colibrium Additive Alain Dupont, Chief Commercial Officer and Staco CEO Byun Sang-don
In March 2023, Innospace became the first domestic space startup to successfully test launch the self-developed private launch vehicle ‘Hanbit-TLV’. The success of the launch also included the role of Staco, a domestic manufacturer that recognized the potential of metal 3D printing and prepared for it. Staco played a major role in the Innospace test launch by successfully developing the oxidant pump for the Hanbit-TLV launch vehicle using only metal 3D printing technology, without any other technology.
The first meeting with Staco took place when Innospace was carrying out a government project, and it received close support from GE Additive in all aspects, including consulting and equipment, and was provided with the know-how and infrastructure to develop an oxidizer pump.
Staco was able to achieve the industrialization of actual metal 3D printing by receiving consulting provided by Colibrium Additive. Even when offline activities were difficult due to the new coronavirus, GE's German and American engineers visited Korea and passed on their know-how and experience in metal 3D printing to Staco and Innospace.
“Unlike other metal 3D printing manufacturers, Colibrium Additive not only develops equipment, but also continuously improves equipment,” said Hyun-guk Jeong, Chief Technology Officer (CTO) and head of the company’s affiliated research center at Staco. “This is because they are directly producing and developing equipment in the aerospace field.” “This is because we can continue to find improvements while doing this,” he explained.
Numerous fields of application… Metal 3D printing technology for use in the space field is just beginning.
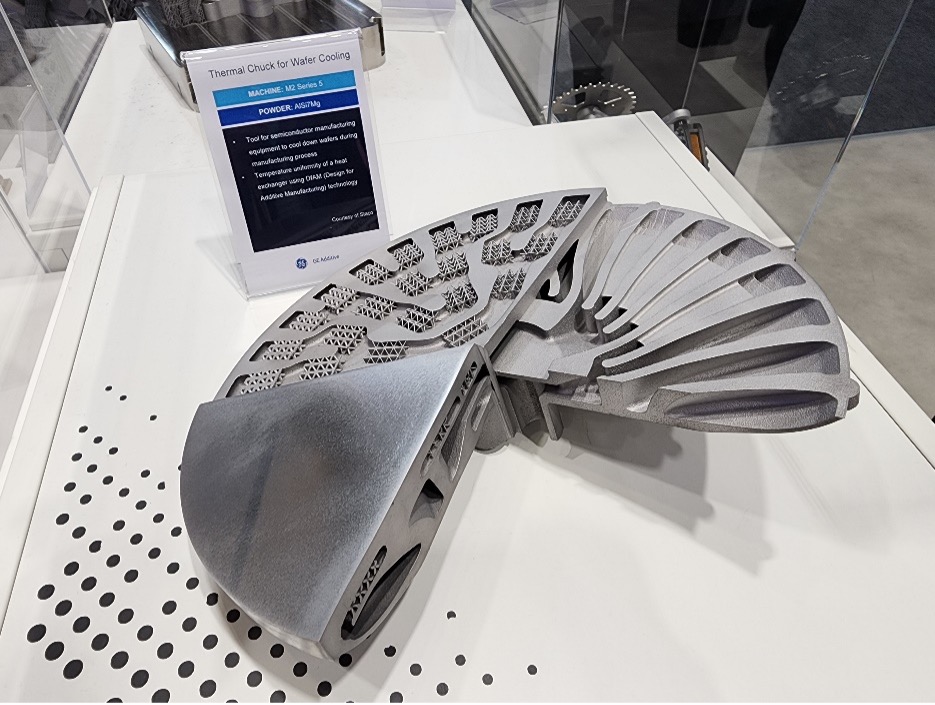

Thermal Chuck developed and produced by Staco through Colibrium Additive's M2 Series 5
Staco was originally a company that produced vacuum chambers for making semiconductor displays such as Samsung Electronics. In the second half of 2017, while reviewing new businesses, the company showed interest in the aerospace field and began investing heavily as it was expected that great synergy would be created by combining metal handling and metal 3D printing.
Through its work with with Colibrium Additive, Staco was able to grow to a high level in a short period of time in the domestic metal 3D printing industry. “On average, it takes at least 5 years to enter the domestic aerospace field as a first-tier vendor, but Staco was able to settle down quickly in just 3 years,” said Hyun-guk Jeong, chief technology officer at Staco. “We have many metal 3D printers,” he explained. Staco currently has four Colibrium Additive M2 units and one large X Line model and is making efforts to expand its diverse equipment portfolio.
All parts developed by Staco for the Innospace test launch vehicle were developed and produced using metal 3D printing technology. Rocket engines have a complex structure and require detailed design and extensive testing to satisfy factors such as high temperature, low temperature, and high pressure. For this reason, a large amount of prototypes must be created and tested, and complex processes such as the development period take a lot of time. For example, when combining parts using the casting method, a wooden mold is created, and a single part is completed through a method of attaching forged plate-shaped materials and welding them at high heat. However, using metal 3D printing technology, it can be made from a single designed part, simplifying this process and shortening the development and production period. In addition, because the process for each small part (part) can be done in one place, logistics costs and infrastructure costs in the supply chain are reduced.
Staco plans to continue to strengthen collaboration with Innospace in the future and expand beyond the aerospace field to the automotive and medical fields. Staco's vision is to become the best 3D printing manufacturer by creating an automated AM factory (Additive Manufacturing) in the future. Staco CEO Byun Sang-don said, “We are looking forward to continuing our strategic workwith Colibrium Additive in the future.”
Additional Information:
GE Additive recently rebranded as Colibrium Additive. This new name combines the two English words ‘collaboration’ and ‘equilibrium’ and reinforces the company’s approach leading the additive industry from the front—be that educating regulators, partnering with academia, and fostering the next generation of additive talent. As a proven leader in the additive industry the company will continue to offer trusted, balanced viewpoints and pragmatism as the industry evolves and experiences change.
-
금속 3D프린팅…이제는 우주로 쏘아올린다
적층제조(금속 3D프린팅) 기술은 기존 폴리머를 활용한 3D프린팅 기술에 대한 관심을 끌면서 동시에 차세대 기술로 각광받아왔다. 실제 항공분야에서 기술이 사용되면서 적층제조의 활용 범위 또한 매우 넓어졌지만 아직 금속 3D프린팅 기술은 선진 기술로 국내에서는 인프라, 활용 범위, 기술의 이해도 등은 타 선진국과 비교해서 뒤떨어지고, 실제 관련 전문 교육이나 과정 등이 부족한 실정이다.
이러한 점을 보완하기 위해 금속 3D프린팅 분야에 선두주자인 콜리브리엄 애디티브(전 GE 애디티브)의 경우 포괄적인 원스톱 서비스를 제공한다. 실제 산업화에 도움이 될 수 있도록 교육을 포함한 컨설팅부터 재료 제공까지 다양한 지원을 아낌없이 제공한다. 컨설팅의 경우 ‘디스커버리 워크샵(Discovery Workshop)’이라는 금속 3D프린팅 산업 및 기본에 대한 내용을 고객사에게 공유하고, 이후 심화과정인 ‘디자인 워크샵(Design Workshop)’, 실제 산업화 단계에 필요한 각종 프로세스에 대한 과정인 ‘인더스트리얼라이제이션 워크샵(Industrialization Workshop)’까지 제공을 한다.
뿐만 아니라 GE가 인수한 AP&C의 금속분말(재료)를 제공하기 때문에 수준 높은 품질의 제품을 완성 시킬 수 있다. AP&C의 분말들은 가스 방식으로 만드는 타 분말 제조사와 달리 플라즈마 방식으로 구형 분말을 만들기 때문에 품질이 뛰어나다.
실제 콜리브리엄 애디티브의 이러한 원스톱 서비스를 활용하여 금속 3D프린팅을 활용한 산업화 사례가 나오고 있다. 최근에 각광받고 있는 우주 분야 역시 금속 3D프린팅 기술의 접목을 통해 국내 기업들은 발 빠른 성장을 이루어 내고 있다.
스타코, 국내 금속 3D프린팅 기술 … 국내 최초 민간 로켓 발사 성공 기여
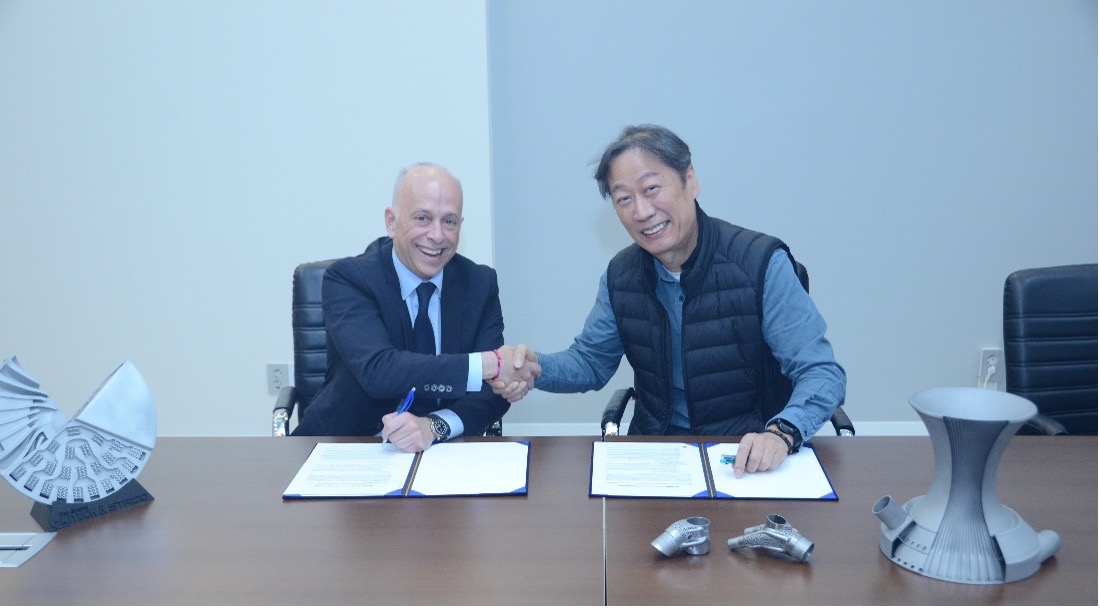

사진설명 = 콜리브리엄 애디티브 알레인 듀퐁 최고상업책임자(Alain Dupont, Chief Commercial Officer) 및 스타코 변상돈 대표가 업무협약을 맺고 있다)
2023년 3월 이노스페이스는 국내 우주 스타트업 최초로 자체 개발한 민간 발사체 ‘한빛-TLV’ 시험발사를 성공시켰다. 발사 성공에는 금속 3D프린팅에 대한 가능성을 알아보고 준비한 국내 제조업체 ‘스타코(Staco)’의 역할도 컸다. 스타코는 한빛-TLV 발사체의 산화제 펌프를 다른 기술 없이 오로지 금속 3D프린팅 기술로만 개발을 성공하여 이노스페이스 시험발사에 큰 역할을 했다.
스타코는 이노스페이스의 정부 과제를 수행할 때 첫 만남이 이루어졌고, GE 애디티브로부터 컨설팅, 장비 등까지 모든 부분에 대해서 긴밀한 지원이 있었고 산화제 펌프를 개발 할 수 있는 노하우와 인프라를 제공 받았다.
스타코는 콜리브리엄 애디티브가 제공하는 컨설팅을 받으면서 실제 금속 3D프린팅의 산업화를 이루어낼 수 있었다. 신종코로나 바이러스로 인해 오프라인 활동이 어려운 시점에서도 콜리브리엄 애디티브의 독일 및 미국 엔지니어들이 방한하여 스타코와 이노스페이스에게 금속 3D프린팅에 대한 노하우와 경험을 전수해줬다.
스타코 정현국 최고기술책임자(CTO)겸 기업부설 연구소장은 “콜리브리엄 애디티브는 다른 금속 3D프린팅 제조사와 달리 장비 개발만 하는 것이 아니라 장비 개선이 꾸준히 되고 있다” 며 “이는 자신들이 항공우주분야에서 직접 생산 개발을 하면서 계속해서 개선점을 찾아 낼 수 있기 때문”이라고 설명했다.
수많은 활용 분야…우주 분야에 활용할 금속 3D프린팅 기술은 이제 시작
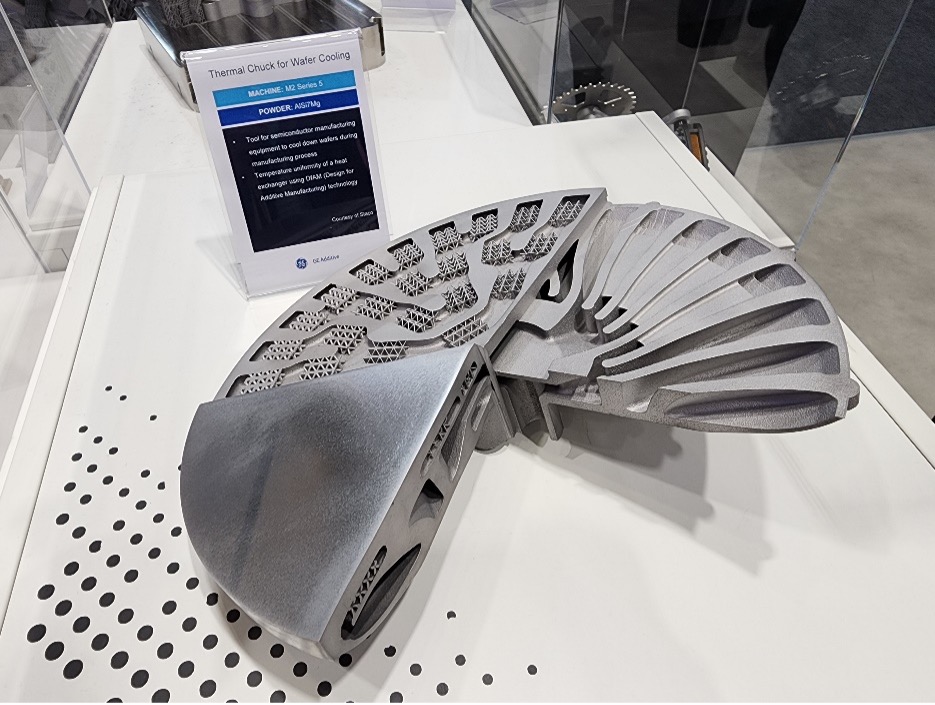

(사진설명 = 스타코가 콜리브리엄 애디티브의 M2 시리즈 5를 통해 개발 및 생산한 서멀 척(Thermal Chuck)
스타코는 본래 삼성전자 등 반도체 디스플레이를 만들기 위한 진공체임버를 생산하는 기업이었다. 2017년 하반기에 들어서서 신사업을 검토하다가 항공우주분야에 관심을 보이고 금속을 다루는 일과 금속 3D프린팅을 접목하면 큰 시너지가 날 것으로 예상되어 집중 투자하기 시작했다.
스타코는 콜리브리엄 애디티브와의 협업을 통해 국내 금속 3D프린팅 업계에서 짧은 시간에 높은 수준으로 성장할 수 있었다. 스타코 정현국 최고기술책임자는 “평균적으로 새롭게 국내 항공우주 분야에 1차 벤더(vendor)로 진입할 때는 빨라야 최소 5년이 걸리는데 스타코는 3년만에 빠르게 안착할 수 있었다” 며 “현재 국내 중소기업 기준으로 가장 많은 금속 3D프린터를 보유 하고 있다”고 설명했다. 스타코는 현재 콜리브리엄 애디티브의 M2 4대 및 대형 기종인 XLine 1대를 구비하고 있으며 다양한 장비 포트폴리오 확장을 위한 노력을 기울이고 있다.
이번 스타코가 이노스페이스 시험발사체를 위해 개발한 부품은 모두 금속 3D프린팅 기술로 개발되어 생산되었다. 로켓 엔진은 복잡한 구조로 구성되어 있고 고온ㆍ저온 및 고압 등 요소를 만족시키기 위해 세밀한 설계가 필요하며 테스트를 많이 해야한다. 이런 이유로 많은 양의 시제품(프로토타입)을 만들어서 테스트 해야 하고 개발 기간 등 복잡한 공정으로 시간이 많이 소요된다. 예를 들어 주조 방식으로 부품을 조합할 경우 목형을 만들고, 단조판형 소재를 붙여 고열로 용접하는 공법을 통해 하나의 부품이 완성된다. 하지만 금속 3D프린팅 기술을 활용하면 바로 설계된 하나의 부품으로 만들 수 있기 때문에 이런 공정을 단순화하여 개발기간 및 생산기간이 앞당겨진다. 또한, 각 소부품(파트)에 공정이 한곳에서 가능해지기 때문에 공급망사슬에서의 물류비용 및 인프라 비용도 줄어든다.
스타코는 향후 이노스페이스와 지속적인 협업을 강화해갈 예정이며, 우주항공 분야를 넘어서 자동차, 의료 분야까지도 확장을 할 예정이다. 스타코는 향후 자동화 AM 팩토리(Additive Manufacturing)를 만들어 최고의 3D프린팅 제조사가 되는 비전을 그리고 있다. 스타코 변상돈 대표이사는 “콜리브리엄 애디티브와 전략적 제휴를 통해 지속적인 협업을 기대하고 있다” 며 “향후 콜리브리엄 애디티브와 여러 방면에서 협업하기를 바란다”고 밝혔다.
참고:
GE Additive는 최근 Colibrium Additive로 브랜드가 변경되었다. 새로운 이름은 'collaboration'과 'equilibrium'이라는 두 영어 단어를 결합하여 규제 기관을 교육하고, 학계와 협력하고, 차세대 적층 인재를 양성하는 등 적층 산업을 전면적으로 선도하는 회사의 접근 방식을 나타낸다. 적층제조 산업의 입증된 리더로서 회사는 업계가 발전하고 변화를 경험함에 따라 신뢰할 수 있고 균형 잡힌 관점과 실용주의를 계속해서 제공할 예정이다.